In this post, i will guide you on how to create a serverless function in AWS that automatically stops and starts EC2 instances or VMs on a schedule (e.g., stop at 7 PM, start at 8 AM on weekdays).
Business Problem: Reducing cloud costs by shutting down non-production resources when they are not in use.
What you’ll learn: Serverless computing, IAM roles/Managed Identities, scheduling, and cost management fundamentals.

Automate Start/Stop of EC2 Instance using Server-less Function
Services Used :
- Lambda
- EventBridge (for scheduling)
- IAM
- EC2
I will create a Stop schedule using Amazon EventBridge and use a Lambda function to read which action to perform from the event sent by the schedule.
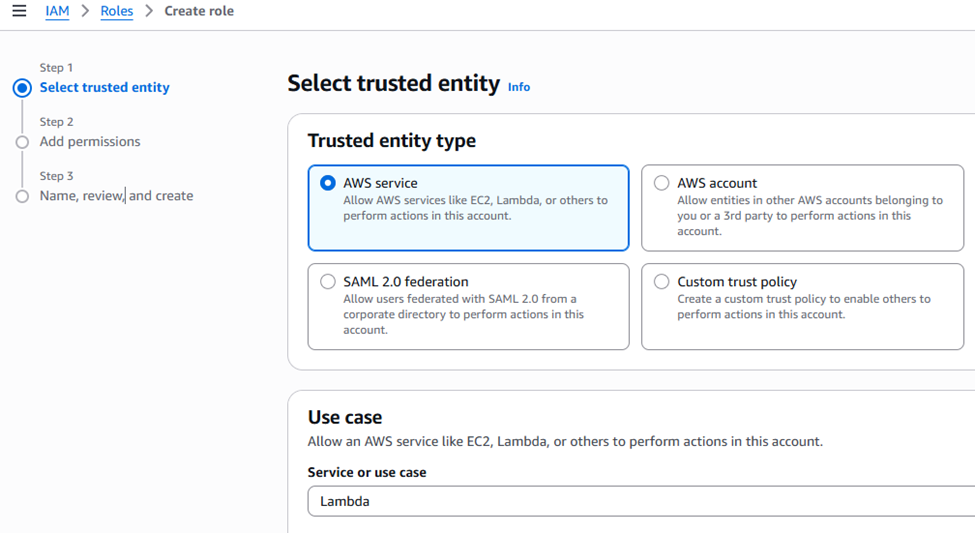
Step 1: Create an IAM Role for the Lambda Function
The Lambda function needs permission to describe, start, and stop EC2 instances.
- Navigate to IAM: In the AWS Console, go to the IAM service.
- Roles: Click on “Roles” in the left menu, then “Create role”.
- Trusted entity type: Select “AWS service”.
- Use case: Select “Lambda” and click “Next”
- Role name:
EC2-Scheduler-Lambda-Role. - Create role: Click “Create role”.
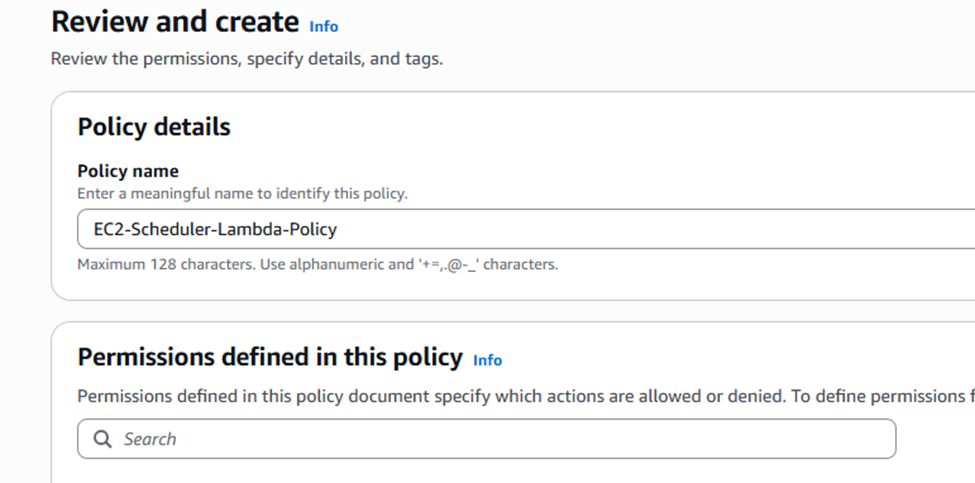
Add permissions: We need to create a custom policy. Click “Create policy” in a new tab.
- In the policy editor, switch to the JSON tab.
- Paste the below policy given in JSON. This grants the minimum required permissions.
- Click “Next: Tags”, then “Next: Review”.
- Name:
EC2-Scheduler-Lambda-Policy. - Click “Create policy”.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ec2:DescribeInstances",
"ec2:StopInstances",
"ec2:StartInstances"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
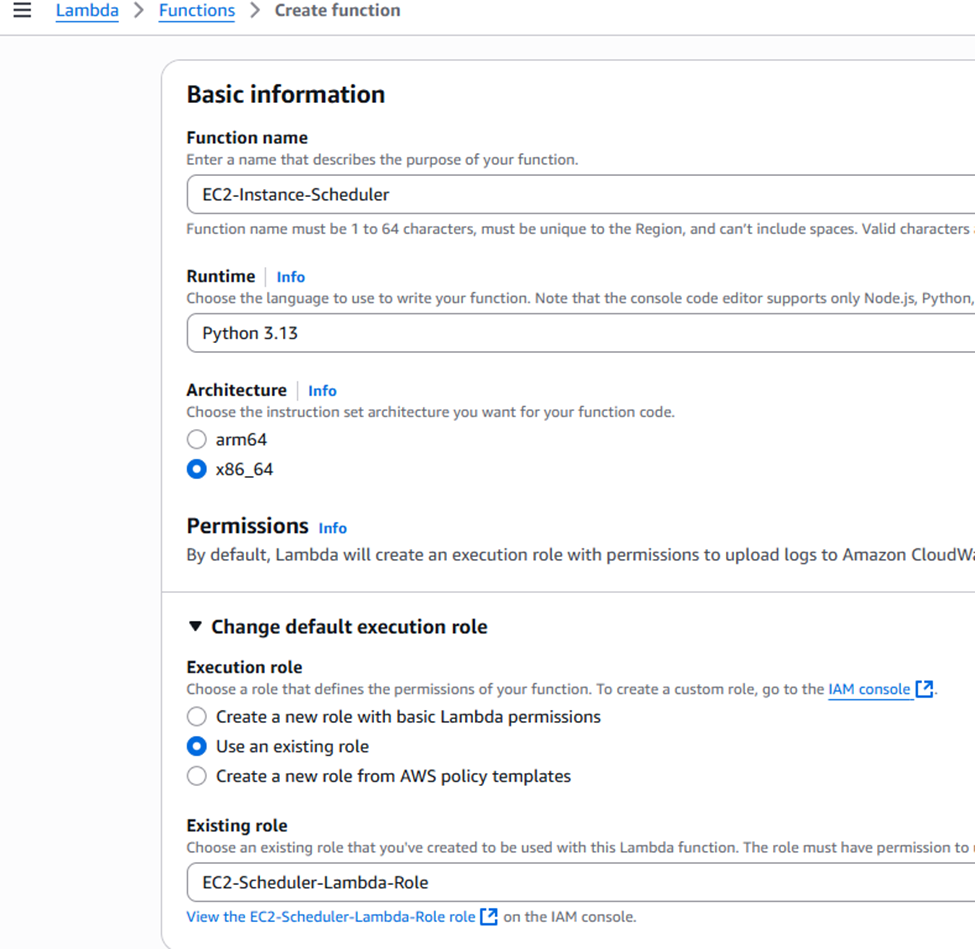
Step 2: Create the Lambda Function
This function contains the logic to check instance tags and perform the start/stop action.
- Navigate to Lambda: Go to the Lambda service in the console.
- Create function: Click “Create function”.
- Author from scratch:
- Function name:
EC2-Instance-Scheduler. - Runtime: Select Python 3.9 (or a later Python version).
- Architecture:
x86_64. - Permissions: Expand “Change default execution role”. Select “Use an existing role” and choose the
EC2-Scheduler-Lambda-Roleyou just created.
- Function name:
- Create function: Click “Create function”.
- Add the Code: In the “Code source” editor, replace the default code with the below given Python script
- Deploy: Click the “Deploy” button to save your code.
import boto3
import os
# Initialize the EC2 client
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2')
def lambda_handler(event, context):
"""
Main function for the Lambda handler.
This function is triggered by an EventBridge schedule. It scans EC2 instances
for a specific tag ('Scheduler') and performs a start or stop action based
on the 'action' passed in the event payload from EventBridge.
"""
# Get the action ('start' or 'stop') from the EventBridge event
action = event.get('action')
if not action or action.lower() not in ['start', 'stop']:
print("Error: 'action' not provided or invalid in the event. Must be 'start' or 'stop'.")
return
print(f"Action requested: {action.upper()}")
# Define the filter to find instances with the 'Scheduler' tag set to 'active'
filters = [
{
'Name': 'tag:Scheduler',
'Values': ['active']
}
]
# Retrieve instances that match the filter
response = ec2.describe_instances(Filters=filters)
instance_ids_to_process = []
# Iterate through reservations and instances
for reservation in response['Reservations']:
for instance in reservation['Instances']:
instance_id = instance['InstanceId']
instance_ids_to_process.append(instance_id)
if not instance_ids_to_process:
print("No instances found with tag 'Scheduler:active'. Exiting.")
return
print(f"Found instances to {action}: {instance_ids_to_process}")
# Perform the start or stop action
if action.lower() == 'start':
print("Starting instances...")
ec2.start_instances(InstanceIds=instance_ids_to_process)
print("Successfully sent start command.")
elif action.lower() == 'stop':
print("Stopping instances...")
ec2.stop_instances(InstanceIds=instance_ids_to_process)
print("Successfully sent stop command.")
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'body': f"Successfully processed {action} for instances: {instance_ids_to_process}"
}Step 3: Create EventBridge Schedules
We’ll create two rules: one to start instances and one to stop them.
A. Create the “Stop” Rule (Evening)
- Navigate to EventBridge: Go to the service in the console.
- Create rule: Click “Create rule”.
- Name:
Stop-EC2-Instances-Evening. - Rule type: Select “Schedule” and click “Next”.
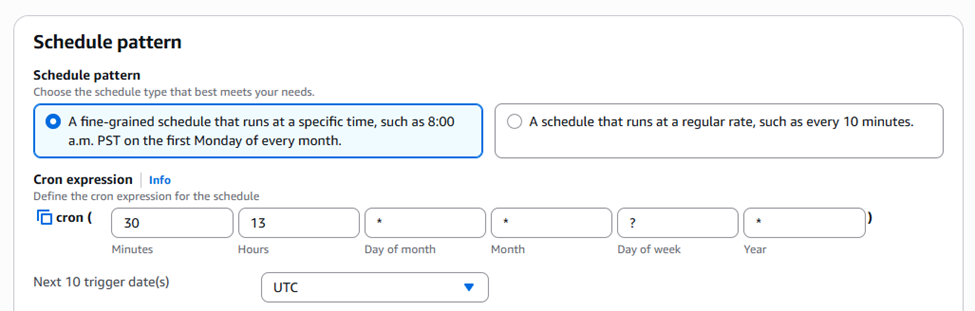
- Schedule pattern:
- Select “A schedule that runs at a regular rate…”
- Choose “Cron expression”.
- For the expression, enter
30 13 * * ? *(This runs at 1:30 PM UTC every day. Adjust the time as needed. The cron is inmin hour day-of-month month day-of-week year).
- Next: Click “Next”.
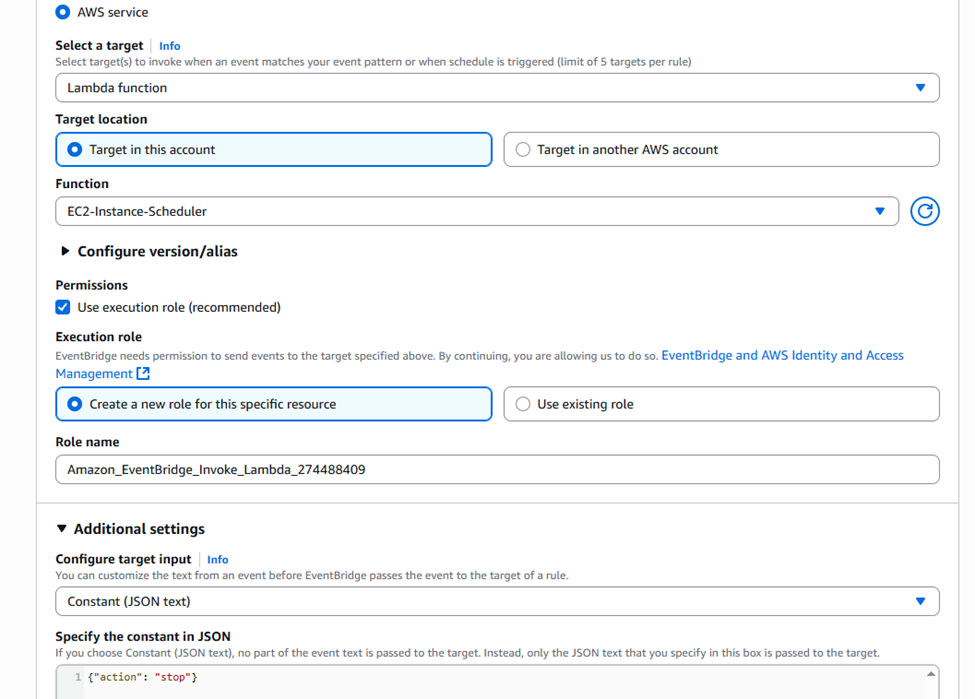
- Select a target:
- Target types: “AWS service”.
- Select a target: “Lambda function”.
- Function: Select the
EC2-Instance-Schedulerfunction.
- Configure input (IMPORTANT): Expand “Additional settings”.
- Select “Constant (JSON text)”.
- In the text box, enter:
{"action": "stop"}. This tells our function what to do. ( For start rule , have the action as ‘start’).
- Next -> Next -> Create rule.
Similarly, you can create a rule for starting the instance and have the time as 8AM . This way both start and stop of EC2 instance is automated.
The given python script already handles Start and Stop actions.
Step 4: Tag Your EC2 Instances
The final step is to tell the scheduler which instances to manage.
- Navigate to EC2: Go to your EC2 dashboard.
- Select an instance: Check the box next to an instance you want to schedule.
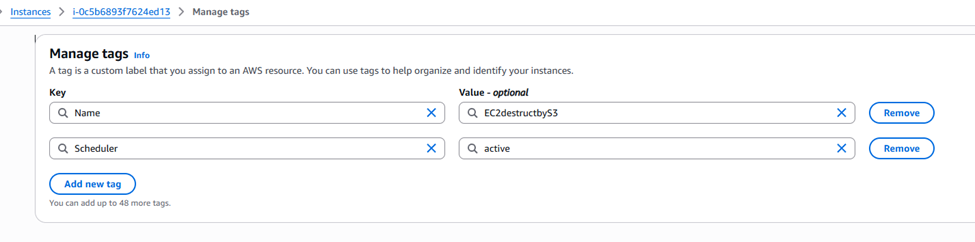
- Manage tags: Click the “Tags” tab in the bottom panel, then “Manage tags”.
- Add tag:
- Key:
Scheduler - Value:
active
- Key:
- Save.
Now, your setup is complete! The EventBridge rules will trigger the Lambda function at the scheduled times, and the function will only start or stop the instances that have the Scheduler:active tag.
As highlighted earlier, you can create one more rule to ‘Start’ the EC2 instance and follow the same steps to automate the complete lifecycle of an EC2 Instance.